Associated Press
WASHINGTON (AP) — U.S. officials are reporting two more deaths and additional cases of vision loss linked to eyedrops tainted with a drug-resistant bacteria.
The eyedrops from EzriCare and Delsam Phama were recalled in February and health authorities are continuing to track infections as they investigate the outbreak.
In the latest government tally, 68 people were diagnosed with infections from the bacteria, which has now caused a total of three deaths and eight cases of people losing their vision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported on Tuesday. That’s up from one death and five cases of permanent vision loss reported last month.
The CDC said four people have undergone surgery to remove an eyeball due to the infections.
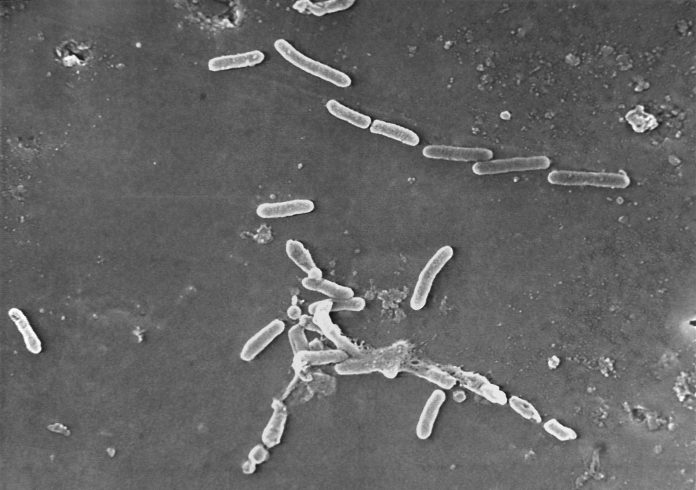
The outbreak is considered particularly worrisome because the bacteria driving it is resistant to standard antibiotics.
The CDC has now identified cases in 16 states, including California, New York, Illinois, Texas and Pennsylvania. Most of the cases have been linked to four regional clusters and Ezricare’s drops are the only product used by patients in each of those groups.
The recalled drops were manufactured by Global Pharma Healthcare in India, where the bacteria — Pseudomonas aeruginosa — is commonly linked to outbreaks in hospitals. It can spread through contaminated hands or medical equipment.



















