At a time when counties, cities and states across the South are removing or covering up Confederate monuments, one of the world’s largest paintings of the American Civil War will reopen to the public Friday.
But the artwork was never intended to celebrate the Confederacy, historians say.
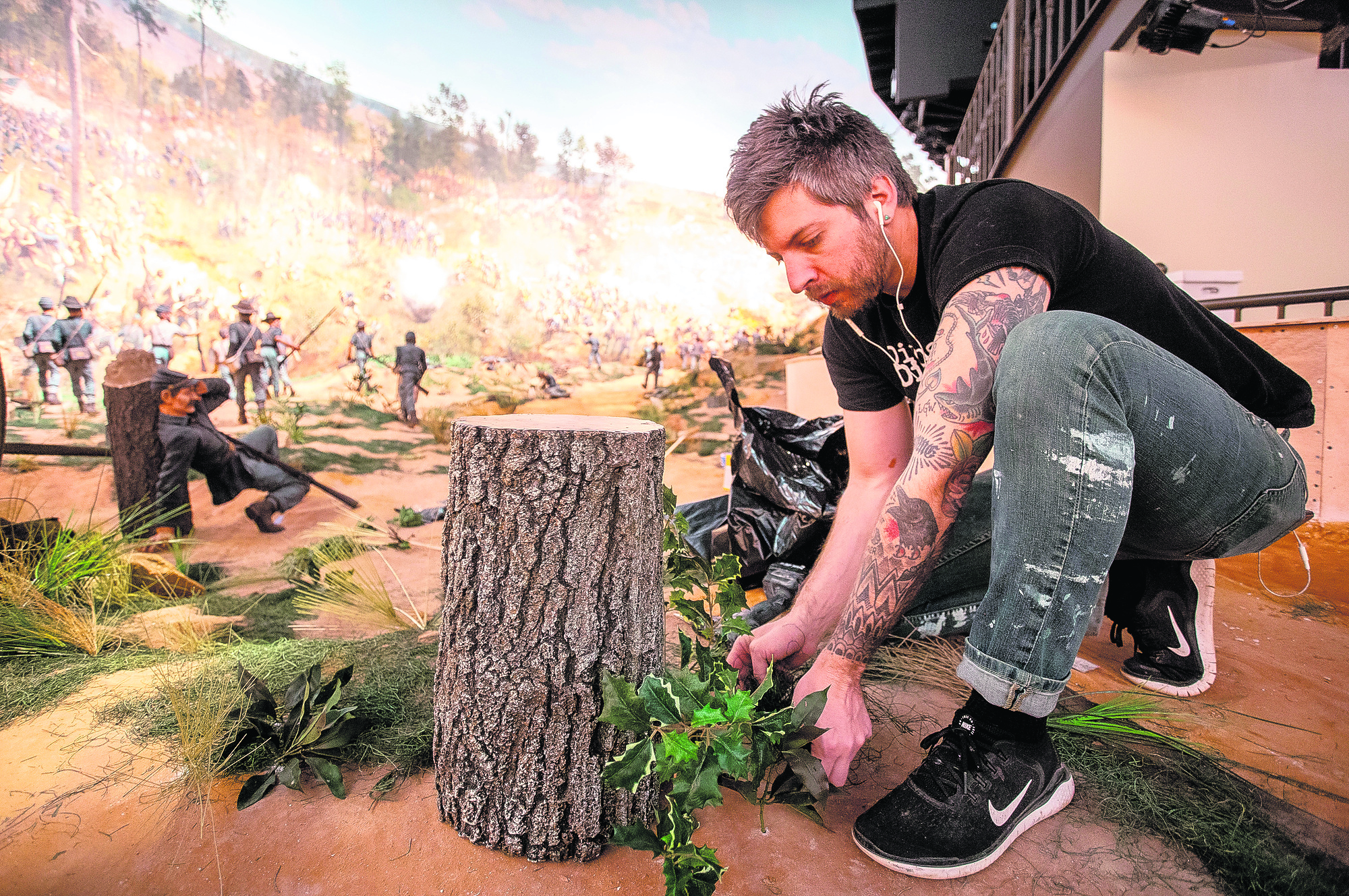
Atlanta’s Cyclorama depicts charging horses, wounded soldiers, cannon blasts and smoke on a Civil War battlefield in Atlanta as Union troops defeated Confederate forces and then torched much of the city.
The painting also takes viewers into another, more personal battlefield in the mind’s eye, this one involving memory, facts, fiction, propaganda and romanticized portrayals of history, historians say.
The German immigrants who painted it at the American Panorama Company in Milwaukee were creating the work for a northern audience to celebrate a northern victory in the Battle of Atlanta.
“So when people are concerned about Confederate monuments — those who want to hug them and those who want to tear them down — they’re both going to be surprised to find out it’s not one,” said Sheffield Hale, president and CEO of the Atlanta History Center. “And that’s when you have the opportunity for insight and learning.”
DIVERGING VIEWS OF HISTORY
The painting was created about 22 years after the Battle of Atlanta had occurred in 1864. It debuted in Minneapolis in 1886.
When the artwork was relocated to Atlanta in 1892, Confederate sympathizers focused on the valor and bravery displayed by their side, said Gordon Jones, senior military curator at the history center. It was advertised in Atlanta as “the only Confederate victory ever painted.”
“It’s one of the greatest pieces of spin that’s ever been put on an artifact,” Jones said.
Though the painting depicts a northern victory, southerners saw in the painting an Atlanta rising like the mythical phoenix — the symbol still used on police cars and city buildings today.
“The more you learn about this painting, the more remarkable is the story,” Jones said. “And the story is definitely one of an artifact that changes meaning over time, depending on how you look at it.”
IMAX MOVIES OF THEIR DAY
Before Hollywood movies, cycloramas such as the “Battle of Atlanta” were considered the virtual reality of their day.
“It’s intended to surround you, to be this sort of virtual reality time machine,” Jones said.
After they were painted in cities such as Milwaukee and Chicago, cycloramas were rolled up and hauled by train around the country. People in various cities then paid admission to walk into specially built round buildings to view them.
The Atlanta History Center built the massive Lloyd and Mary Ann Whitaker Cyclorama Building to display the painting. Inside is a 15-foot (4.6-meter) platform, allowing visitors to view the horizon at eye level, with a massive blue sky above and the battle unfolding beneath them. A canopy covers the observation platform, much like canopies were used in the 19th century displays.
“We have returned the painting to its original intent in 1886, and it was intended as an illusion, it was intended as mass entertainment,” Jones said. “Nobody has seen this painting the way it was originally intended to be seen in 1886.”
ONE OF THE WORLD’S LARGEST PAINTINGS
The 360-degree painting is longer than a football field at 371 feet (113 meters); and is nearly 50 feet (15 meters) high. It weighs 10,000 pounds (4,500 kilograms).
When it goes on display again Friday, “The Battle of Atlanta” will join only a handful of giant cycloramas remaining worldwide. Another notable U.S. cyclorama, “The Battle of Gettysburg,” can be viewed at the Gettysburg National Military Park in Pennsylvania.
THE IMMIGRANT ARTISTS
Among the exhibits opening Friday is one about the immigrant painters — mostly German — who battled sea sickness on the steamship that brought them to New York.
To make their scenes as authentic as possible, some of the painters visited battlefields and met with Civil War soldiers in retirement homes before creating their cycloramas in Milwaukee.
Michael Kutzer, a painter and historian who speaks German, has been working in Wisconsin to decipher the hand-written diaries of artist Friedrich Wilhelm Heine, who supervised the cyclorama painters in Milwaukee. That has helped shed light on who they were and their impressions of the United States after arriving from Europe.
THE HISTORICAL CONTEXT
The new exhibit opening Friday also includes early sketches of cycloramas, advertisements, and audio of the tours given from earlier eras. Military artifacts include a wooden chest used by Union General James McPherson, who died in the Battle of Atlanta.
Actors who play characters from history will also provide context, Hale said. They include Paul Atkinson, the Georgia entertainment promoter who brought the painting to Atlanta, who explains how he interpreted the artwork for southern audiences.
On the red clay landscape beneath the painting, the history center has also restored the 128 soldier figures on the “diorama” beneath the painting. Those figures include a fallen Union soldier that was created in the likeness of actor Clark Gable after his visit to the Cyclorama when “Gone With the Wind” premiered in Atlanta in 1939.q